문제 :
원을 추상화한 Circle 클래스는 간단히 아래와 같다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
class Circle{
int radius;
public:
Circle(int radius=0) { this->radius = radius; }
void show() { cout << "radius = " << radius << " 인 원" << endl; }
};
|
다음 연산이 가능하도록 연산자를 프렌드 함수로 작성하라.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
Circle a(5), b(4);
++a; // 반지름을 1 증가 시킨다.
b = a++; // 반지름을 1 증가 시킨다.
a.show();
b.show();
|
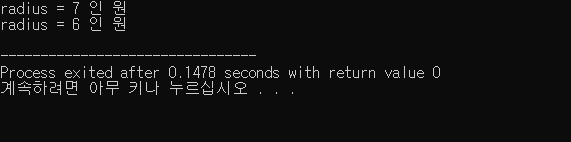
실행 결과 :
목적 및 힌트 :
프렌드 함수로 연산자 구현 연습
코드 :
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Circle{
int radius;
public:
Circle(int radius=0) { this->radius = radius; }
void show() { cout << "radius = " << radius << " 인 원" << endl; }
friend Circle& operator++(Circle& c);
friend Circle operator++(Circle& c, int x);
};
Circle& operator++(Circle& c){
c.radius++;
return c;
}
Circle operator++(Circle& c, int x){
Circle test = c;
c.radius++;
return test;
}
int main() {
Circle a(5), b(4);
++a; // 반지름을 1 증가 시킨다.
b = a++; // 반지름을 1 증가 시킨다.
a.show();
b.show();
}
|
설명 :
전위 ++ 연산과 후위 ++ 연산 모두 참조 매개 변수를 사용하고 전위 연산자의 경우 참조를 리턴합니다.
참조 매개 변수를 사용하지 않는다면, 매개 변수에 복사본이 전달되므로 본래의 값은 변하지 않습니다.
후위 연산자의 int x 매개 변수는 의미 없는 값이고, 이는 후위 연산자와 전위 연산자를 구분하기 위해 전달해주는 매개 변수입니다.
'C++ programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 명품 C++ programming 실습 문제 7장 10번 (3) | 2020.03.06 |
|---|---|
| 명품 C++ programming 실습 문제 7장 9번 (1) | 2020.03.06 |
| 명품 C++ programming 실습 문제 7장 7번 (3) | 2020.03.06 |
| 명품 C++ programming 실습 문제 7장 6번 (1) | 2020.03.06 |
| 명품 C++ programming 실습 문제 7장 5번 (1) | 2020.03.06 |




